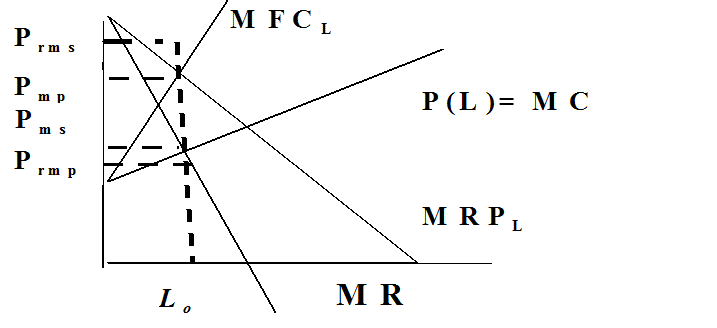28. Correct. The answer is false.
In a bilateral monopoly both players (seller and buyer) desire the
same quantity only if the slopes of the MC and the MRP are equal in absolute
value. Suppose that the monopsony buyer has MRP = a - bL and the monopoly
seller has marginal cost of MC = c + dL. The monopoly
seller wants to set her marginal revenue equal to marginal cost or a - 2bL = c
+ dL. Solving you get Lmp
= (a - c)/(d + 2b). The monopsonist buyer wants to set
MFC = MRP or a - bL = c + 2dL. Solving Lms = (a - c)/(2d+b). Lmp = Lms
when b = d. Here they would want the same quantity but would negotiate on
price. The price would be between their reservation prices Prms
and Prmp, which are described
in problems above.