|
Q22. With which of these sets of policies is a monetarist most likely
to agree:
a. Fine tuning, functional finance
b. Discretionary policy, balancing the budget over the cycle
c. Pegging the interest rate, balancing the full employment
budget
d. Money growing at a constant rate, balancing the budget.
|
|
Q23. From an economist's perspective, which of the following is not
considered to be investment?
a. construction of a new factory
b. purchase of shares of company stock
c. the building of an apartment complex
d. additions to inventories at steel plants
|
|
Q24. The expansion or contraction of business activity which occurs
over a period of time (e.g. 5-10 years) is referred to by economists as:
a. the secular trend.
b. Kondratieff cycles.
c. a business cycle.
d. seasonal variation
|
|
Q25. In which of the following industries or sectors of the economy is
output least likely to be affected by the business cycle:
a. housing construction.
b. automobile production.
c. agricultural commodities.
d. capital goods production.
|
|
Q26. The investment-demand curve will
shift to the left as the result of: 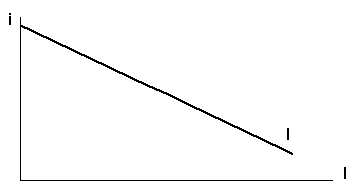
a. business pessimism about future
economic conditions.
b. a shortage of productive
capacity.
c. an increase in the interest
rate.
d. a decrease in business taxes.
|
|
Q27. A single commercial bank must meet a 25 percent reserve
requirement. If it initially has no excess reserves and then $2,000 in cash
is deposited in this bank, it can increase its loans by a maximum of:
a. $2,000.
b. $1,500.
c. $1,250.
d. $1,000.
|
|
Q28. Suppose banks borrow $10 million in reserves from the Fed, and the
reserve requirement is 1/4. What is the maximum change in the money supply
that could take place:
a. $50 million
b. $2.5 million
c. $30 million
d. $40 million
|
|
Q29. Which of the following ways of financing government spending is
the least expansionary?
a. borrowing from the Federal Reserve.
b. borrowing from banks.
c. borrowing from the public.
d. taxation
|
|
Q30. A headline states: ""Real GNP falls again as the economy
slumps."" This situation is most likely to produce what type of
unemployment?
a. frictional
b. structural
c. cyclical
d. natural
|
|
Q31. Stagflation occurs because of a: 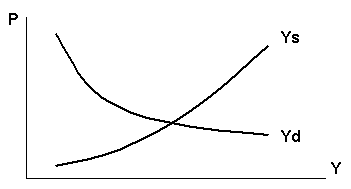
a. rightward shift in the aggregate
demand curve.
b. leftward shift in the aggregate
demand curve.
c. rightward shift in the aggregate
supply curve.
d. leftward shift in the aggregate
supply curve.
|
|
Q32. A new member of congress notes that: ""Personal income tax automatically fall and transfers and subsidies
automatically rise as income declines."" This observation best
describes how the personal income tax transfers and subsidies:
a. serve as a built-in stabilizer.
b. produce the full-employment
budget.
c. cause crowding-out and reduce
equilibrium NNP.
d. contribute to the recognition
lag with fiscal policy.
|
|
Q33. The public debt is the:
a. difference between Federal
assets and liabilities over time.
b. difference between annual tax
revenues and government expenditure.
c. accumulation of Federal budget
surpluses and deficits over time.
d. accumulation of payments for
goods and services purchased by Federal government over time.
|
|
Q34. A budget philosophy that tends to be procyclical
is:
a. functional finance or
discretionary fiscal policy.
b. built-in stabilizers.
c. a cyclically balanced budget.
d. an annually balanced budget.
|
|
Q35. A rise in the international value of
the dollar will tend to:
a. increase exports and reduce
imports.
b. increase exports and increase
imports.
c. reduce exports and reduce
imports.
d. reduce exports and increase
imports.
|
|
Q36. Suppose the need to finance large budget deficits increases
interest rate in the United States. In the diagram FC is foreign currency.
This would most likely: 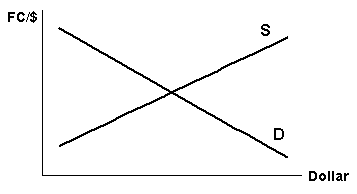
a. increase the foreign demand for
dollars to buy American securities and lower the price of the dollar.
b. increase the foreign demand for
dollars to buy American securities and raise the price of the dollar.
c. decrease the foreign demand for
dollars to buy American securities and lower the price of the dollar.
d. decrease the supply of dollars
to foreign nations to purchase their securities and lower the price of the
dollar.
|
|
Q37. Which set of events would increase the quantity of money demanded
the most?
a. the interest rate increases and nominal GNP increases
b. the interest rate increases and nominal GNP decreases
c. the interest rate decreases and nominal GNP decreases
d. the interest rate decreases and nominal GNP increases
|
|
Q38. If an American can purchase 40,000 pounds for $ 240,000, the
dollar rate of exchange for the pound is one pound equal to:
a. $.60.
b. $4.00.
c. $1.20.
d. $6.00.
|
|
Q39. Suppose that Romulous and the Klingon Empire are the only two planets in the Alpha Quandrant. The following represents the international
accounts for Romulous:
Exports...................................................241
Imports...................................................153
Military spending by Romulous in the Klingon
Empire....... 3
Foreign investment by Romulous in the Klingon
Empire...... 35
Klingon
investment in Romulous............................
14
From these numbers you would conclude that the balance of payments of:
a. Romulous is in deficit.
b. the Klingon
Empire is in deficit.
c. both countries are in balance.
d. the Klingon
Empire is in surplus.
e. a and
d are true.
|
|
Q40. If exchange rates are market
determined and the U.S. inflation rate begins to grow faster than the rates
for other economies, then: 
a. the dollar is likely to
appreciate.
b. the dollar is likely to
depreciate.
c. the U.S. is likely to have a
larger deficit on her balance of payments.
d. the U.S. is likely to have a
smaller deficit on her balance of payments.
|
|
Q41. With which type of inflation do you
get the short-run Phillips Curve trade-off between inflation and
unemployment? 
a. cost-push inflation.
b. structural inflation.
c. price-push inflation.
d. demand-pull inflation.
|
|
Q42. Which of the following would provide a supply of dollars:
a. French demand for California wines
b. Russian purchases of U.S. grain
c. Saudi purchases of U.S. banks
d. U.S. demand for Honda's
e. Japanese investments in VW plants
|
|
Q43. Suppose the total reserves available to the banking sector
(monetary base) are 120 billion, r = 1/10, and banks hold no excess reserves.
If the Fed changes r to 1/16, what is the change in the money supply:
a. -$480 billion.
b. +$480 billion.
c. $1200 billion.
d. $720 billion.
e. none of the above.
|
|
Q44. What is the official unit of account between government central
banks and the IMF?
a. U.S. dollars.
b. high powered money.
c. gold.
d. special drawing rights.
|
|
Q45. Which of the following is true of business cycles?
a. Investment is the most volatile component of GNP.
b. Innovations can contribute to business cycles.
c. The business cycle is influenced by political cycles.
d. All of the above statements are true.
|
|
Q46. Which of the following is not a factor of production?
a. money
b. land
c. labor
d. capital
|
|
Q47. The national income of households consists of the sum of:
a. wages plus rents plus business
interest plus profits.
b. consumption expenditures plus
costs of resources.
c. wages plus salaries.
d. consumption plus investment plus
government spending on goods and services plus exports minus imports.
|
|
Q48. In the simple circular flow model:
a. households are suppliers of
resources and demanders of products.
b. households are suppliers of
products and demanders of resources.
c. businesses are suppliers of
resources and demanders of products.
d. businesses are suppliers of both
resources and products.
|
|
Q49. An unanticipated increase in inflation tends to penalize:
a. people who save money in
financial institutions.
b. individuals who borrow money
from financial institutions.
c. businesses which borrow money
from financial institutions.
d. governments which have a
progressive personal income tax.
|
|
Q50. NATIONAL-INCOME DATA-INCOME
( in billion of dollars)
_________________________________________________________
WAGES AND SALARIES ------------------------------------
141
INDIRECT BUSINESS TAXES
-------------------------------- 32
CAPITAL CONSUMPTION ALLOWANCE
------------------ 16
RENT
------------------------------------------------------------ 8
PROFITS ( GROSS ) -------------------------------------------
70
TRANSFER PAYMENTS
-------------------------------------- 28
INTEREST ( BUSINESS )
--------------------------------------- 4
UNDISTRIBUTED CORPORATE PROFITS
------------------ 13
PERSONAL TAXES -------------------------------------------
25
SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS
---------------------- 9
CORPORATE INCOME TAXES
------------------------------ 14
________________________________________________________
From the above table, what is the Gross National Product?
a. $271
b. $279
c. $307
d. $368
e. over $368
Last updated August 8, 2011.
|