|
Q16. The monopoly's marginal revenue decreases as the quantity sold
increases because
a. the demand curve facing the
monopoly is downward-sloping.
b. the demand curve facing the
monopoly is the market demand curve.
c. the monopoly must reduce price
to entice more customers.
d. all of the above.
e. a and c.
Q17. The monopoly will maximize profit by selling
a. 1 unit.
b. 2 units.
c. 3 units.
d. 4 units.
e. 5 units.
Q18. The price the monopoly will charge is
a. $6.
b. $15.
c. $14.
d. $13.
e. $12.
Q19. Total revenue to the monopoly at the profit-maximizing out-put level
is
a. $60.
b. $42.
c. $30.
d. $52.
e. $16.
Q20. If this were a competitive industry, how many units would be sold?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
Q21.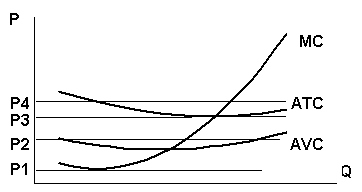 At which price is the firm earning zero economic
profit? At which price is the firm earning zero economic
profit?
a. P1
b. P2
c. P3
d. P4
e. the firm is making economic
profits at all of the above prices.
Q22. Assume the firm is faced with the demand curve at P1 in the above
Figure. Which of the following is true?
a. the firm's revenue are not
covering its variable costs.
b. the firm's fixed costs are less
than its losses.
c. the firm should shut down.
d. all of the above are true.
Q23. A monopsonist is
a. one of the many buyers.
b. one of the many sellers.
c. a sole sellers.
d. a sole buyer.
e. none of the above.
Q24. A lack of competition on either the buying or selling side of the labor
market for the mineral industries results in
a. higher prices for minerals.
b. lower employment opportunities
in mineral industries.
c. less minerals produced.
d. a decrease in the general
welfare of the community.
e. all of the above.
Q25. 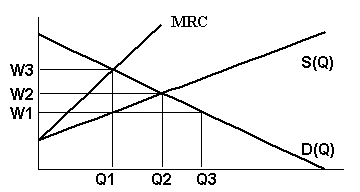 A monopsonist in the graph
to the right will hire A monopsonist in the graph
to the right will hire
a. Q2 workers and pay W2.
b. Q3 workers and pay W1.
c. Q1 workers and pay W3.
d. Q1 workers and pay W1.
e. Q1 workers and pay W2.
Q26. A perfectly competitive labor market in the graph for Q25 will hire
a. Q2 workers and pay W2.
b. Q3 workers and pay W1.
c. Q1 workers and pay W3.
d. Q1 workers and pay W1.
e. Q1 workers and pay W2.
Q27. Which of the following is a characteristic of perfectly competitive
markets?
a. many sellers
b. very small market shares of firms
c. information on prices is freely available
d. freedom of entry and exit
e. all of the above.
Q28. The demand curve faced by perfectly competitive firm:
a. is perfectly inelastic.
b. is horizontal.
c. is downward sloping.
d. is perfectly elastic.
e. b and d.
Q29. The existence of economic profits induces ______ from/into an
industry, which in turn _______ market supply and _______ market price.
a. exiting, increases, increases.
b. exiting, decreases, increases.
c. entry, increases, increases.
d. entry, increases, decrease.
Q30.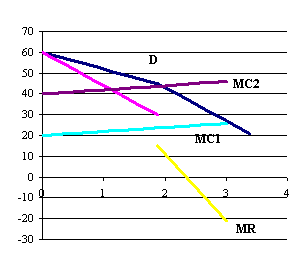 Let the above graph represent a price leadership
model. In this model if a firm raises the price above P1 = 45, no other firms
will raise their price. If a firm lowers their price below P1 all firms will
lower their price.If marginal costs move from MC1
to MC2 then price will: Let the above graph represent a price leadership
model. In this model if a firm raises the price above P1 = 45, no other firms
will raise their price. If a firm lowers their price below P1 all firms will
lower their price.If marginal costs move from MC1
to MC2 then price will:
a. not change.
b. will change from 30 to 45.
c. will change from 25 to 30.
d. will change from 15 to 30.
e. will change from 45 to 50.
Q31.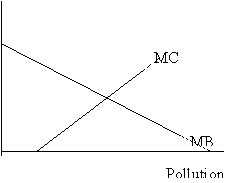 The efficient level of pollution control in the
graph to the right is: The efficient level of pollution control in the
graph to the right is:
a. that level associated with a
zero level of pollution.
b. that level produced by the
market.
c. that level where the marginal
social benefits and marginal social costs of control are equal.
d. at a level where total benefits
equal total costs.
e. none of the above.
Q32. If your income increases from $10,000 per year to $15,000 per year
and your tax payment increases from $2,000 to $4,500, the marginal tax rate
is:
a. 20 %
b. 30 %
c. 50 %
d. not able to be computed.
Q33. If the cross price elasticity of demand for good A and B is positive
you would conclude that the two goods are
a. Giffen goods
b. complements
c. substitutes
d. normal goods
Q34. The individual who brings together economic resources and assumes
risk in a capitalist economy is called:
a. manager
b. entrepreneur
c. Chief Executive Officer
d. chairman of the board
Q35. Which of the following will not cause a change in
demand.
a. change in income.
b. change of the price of the good
in question.
c. change the price of related
goods such as substitutes or complements.
d. expectations of higher prices.
Q36. The figure below contain graphs that show
the demand for and supply of gasoline. Which of the graphs depicts the shift
that would occur as the result of a charge for pollution damage imposed on
the sellers of gasoline?
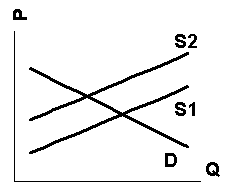 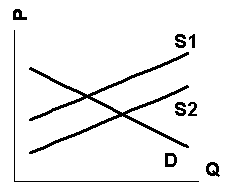 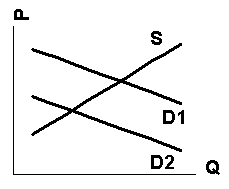
a. graph 1.
b. graph 2.
c. graph 3.
d. none of the above.
Q37. The figure below to the right shows Harry's
marginal benefit schedule for beer consumption. How many six-packs will Harry
purchase each month if the price of a six-pack of a six - pack is $5.50?
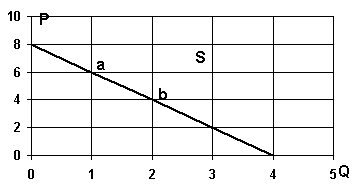
a. 3
b. 4
c. 1
d. 2
Q38. What is the price elasticity of demand between points a and b in the graph for Q37?
a. 1
b. 3
c. 5/3
d. 1/3
Q39. Which of the following is an example of a "market
failure"?
a. there are not enough tickets
available to concerts of extremely popular performers.
b. the price of medical care has
risen dramatically as a result of the introduction of sophisticated equipment
and techniques.
c. polio shots and chest X-rays
provide widespread benefits to the community as a whole as well as to the
individuals who get them.
d. extensive decreases in the
prices of electronic equipment resulted in large numbers of bankruptcies in
the computer industry.
Q40. Suppose you have a two good world with a and
b. If
MUa/Pa < MUb/Pb, you
a. can never maximize utility.
b. have maximized total utility.
c. can increase utility by buying
more of b and less of a.
d. can increase utility by buying
more of a and less of b.
Q41. The production possibilities table given below show how many tons of
either Uranium or Coal can be produced in India
and Canada
with one unit of input. To achieve gains from specialization:
|